Current rating of stranded wire | Comparison between solid and stranded conductors | AWG current rating stranded wire | Current rating of stranded copper wire
When we talk about electrical conductor wireman have two choice first one is solid conductor and second one is stranded conductor.Most of wireman choose stranded conductor due to its advantages over solid conductors.
Here we discuss about how current rating of stranded wire,Comparison between solid and stranded conductors,Current rating of stranded copper wire.
The use of conductors and their insulation is regulated by I E regulations and BIS (ISI) code of practice.
The IE regulations and IS cover all electrical conductors listing the minimum safety precautions needed to safeguard people, buildings and materials from the hazards of using electricity.
Wires and cables are the most common forms of conductors. They are made in a wide variety of forms to suit many different applications
The number of conductors ranges from 3 to 162 and the conductor size varies from 0.193 mm to 3.75 mm diameter depending upon the current carrying capacity and also upon whether these conductors are used in cables or overhead lines
Normally stranded conductors are designated as 10 sq. mm cable of size 7/1.40 where 10 sq.mm gives the area of the cross-section, in the size, numerator (7) gives the number of conductors and the denominator 1.40 gives the diameter of the conductor in mm. Alternatively 7/1.40 cable is the same as 7/17 whereas in the latter case the denominator is expressed in Standard Wire Gauge (SWG) number.
Stranded conductors are more flexible and have better mechanical strength. According to recent stipulation, the cable size should be expressed in sq. millimetres or they can be expressed in terms of the number of conductors in the cable and the diameter of the conductor in mm.
The use of conductors and their insulation is regulated by I E regulations and BIS (ISI) code of practice.
The IE regulations and IS cover all electrical conductors listing the minimum safety precautions needed to safeguard people, buildings and materials from the hazards of using electricity.
Wires and cables are the most common forms of conductors. They are made in a wide variety of forms to suit many different applications
Current rating of stranded wire
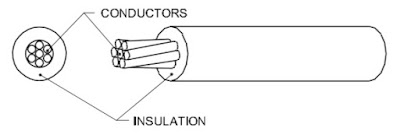
A stranded conductor is one in which there will be a number of smaller sized conductors twisted to form the core as shown in Fig
Normally stranded conductors are designated as 10 sq. mm cable of size 7/1.40 where 10 sq.mm gives the area of the cross-section, in the size, numerator (7) gives the number of conductors and the denominator 1.40 gives the diameter of the conductor in mm. Alternatively 7/1.40 cable is the same as 7/17 whereas in the latter case the denominator is expressed in Standard Wire Gauge (SWG) number.
Stranded conductors are more flexible and have better mechanical strength. According to recent stipulation, the cable size should be expressed in sq. millimetres or they can be expressed in terms of the number of conductors in the cable and the diameter of the conductor in mm.
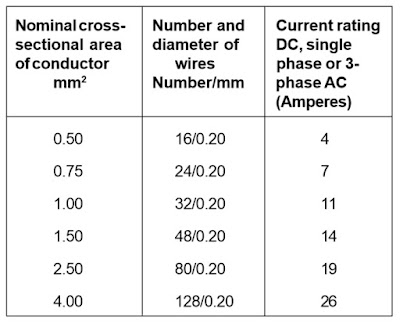
From above table we can say 1 sq.mm wire have 32 no of strands of 0.20 mm diameter conductors. Its current caring capacity is up to 11 Amps safely.
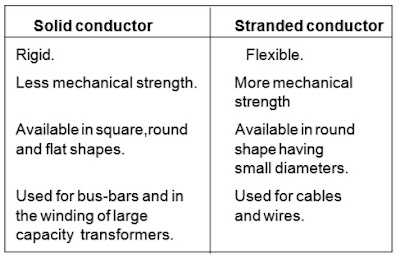
Comparison between solid and stranded conductors
As stranded conductors are more flexible, chances of break of conductors and crack of insulation at the bend is less. They can be easily handled and laid. Connections and joints of stranded conductors are stronger and have longer life.
In stranded conductors the insulation has a better grip on the wire.Solid conductors between supports of overhead lines may break due to vibration.
This breakage is less in stranded conductors. The space between the strands permits flow of oil in UG cables enabling better insulation properties and cooling.
For a given area of cross- section stranded cables carry more current than solid conductors.
This is my view on Current rating of stranded wire,Comparison between solid and stranded conductors,AWG current rating stranded wire,Current rating of stranded copper wire after doing research.please give your view in comments.
Thank you


ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon